Melon aphid (Aphis gossypii);
Green peach aphid (Myzus persicae);
Blueberry oat aphid (Pieris brassicae).
Sweet pepper, cucumber, eggplant, rose, glasshouse chrysanthemum.
30 ml vial contains 250 individuals;
30 ml vial contains 500 individuals;
250 ml vial contains 1000 individuals;
blisters 10 psc. by 100 psc. contains 1000 individuals.
Aphidius colemani is a tiny parasitic wasp (about 2 mm), that stings its aphid victim. The body is black with brown legs, long antennae, and veined wings. The female has an oblong abdomen, while the male has a circular one.
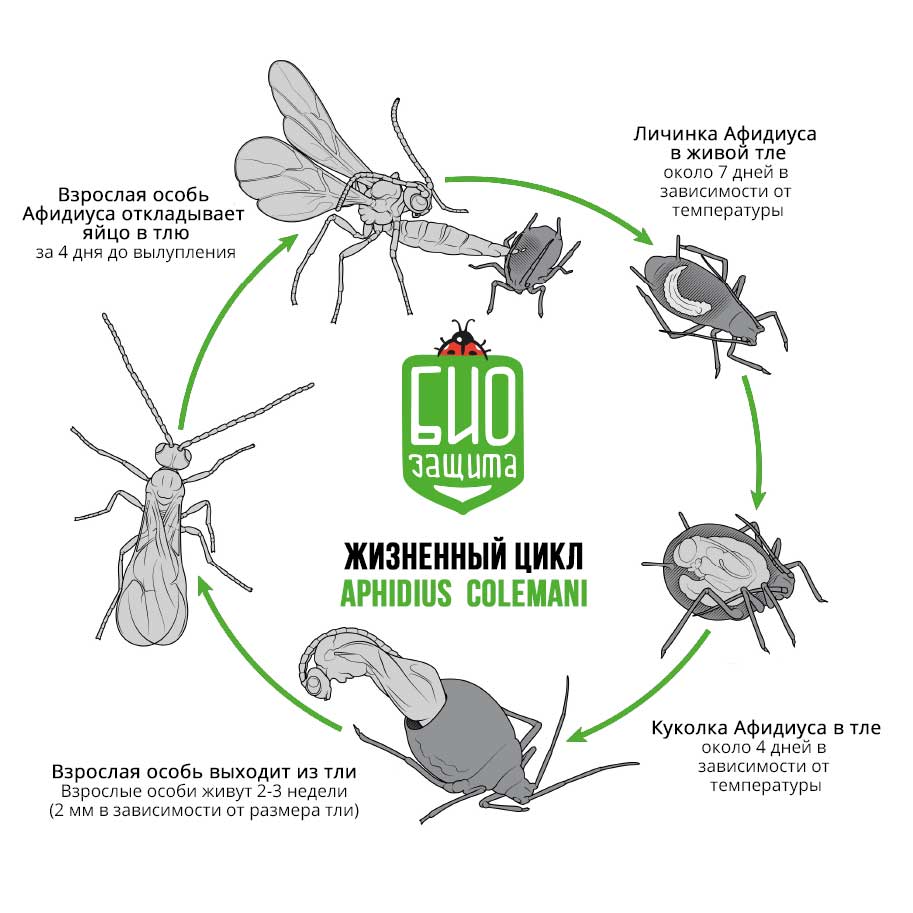
The female deposits its egg in the aphid, where it passes through 4 larval instars. As soon as the larvae development has been completed, the larva rotates inside the pest cuticle, causing it to swell.
A. colemani eggs hatch into larvae which feed on the contents from the inside. In the beginning, the larva doesn’t kill the host and allows the aphids to grow to the desired size. After 6 to 7 days, the larva grows significantly and consumes aphid.
Аfter the 7th day of infection the larvae fixates the aphid on the leaf and forms a cocoon inside the body. On the outside the aphid becomes golden-brown color, this instar is called the mummy.
After the 4th day of mummification, the adult leaves the mummy through a hole. The total life cycle takes 14 days at 21°C and 10 days at 25°C.
During lifecycle, the female lays about 100 eggs. Life span is 2-3 weeks. The ratio of females to males is approximately 2: 1
| Bioagent in Latin | Prevention | Doses of the application by infection degree | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Average | High | ||
| Aphidius colemani | 0.25 ind/m2 | 1 ind/m2 | 2 ind/m2 | 3 ind/m2 |
| Frequency | once in a month | in a week | weekly | weekly |








Оставить комментарий