Red spider mite (Tetranychus urticae);
Red fruit mite (Panonychus ulmi
Citrus red mite (Panonynchus citri
Citrus silver mite (Polyphagotarsonemus latus);
Cyclamen mite (Tarsonemus pallidus
cucumber, tomato, ornamental (rose), fruit (strawberry, grape.
1 litre - bottle;
5 litre -рlastic bucket;
box of 500 hooked - sachets (paper / foil);
50 - meter tape of hooked sachets.
The female is oval-shaped and has 4 pairs of legs, its length of about 0.5 mm. The body is pale yellowish in color but can vary from orange to bright reddish-orange depending on feeding. The legs are relatively long, especially the front pair. The dorsal shield has 17 pairs of setae, the posterior pair is somewhat longer and sharp-tipped. Spermateca (receptaculum seminis) has a bell-shaped calyx. There are 3 teeth on the movable cheliceral digit, on the fixed digit there are 4 distal and 2 basal teeth. Males are smaller than females, their chelicera has a specific form of spermatodactyl.
A. californicus’ life cycle has a standard type of ontogenesis for parasitoid mites with successively changed developmental instars: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph, adult (female or male). The female prefers to lay eggs in a colony of spider mites.
.
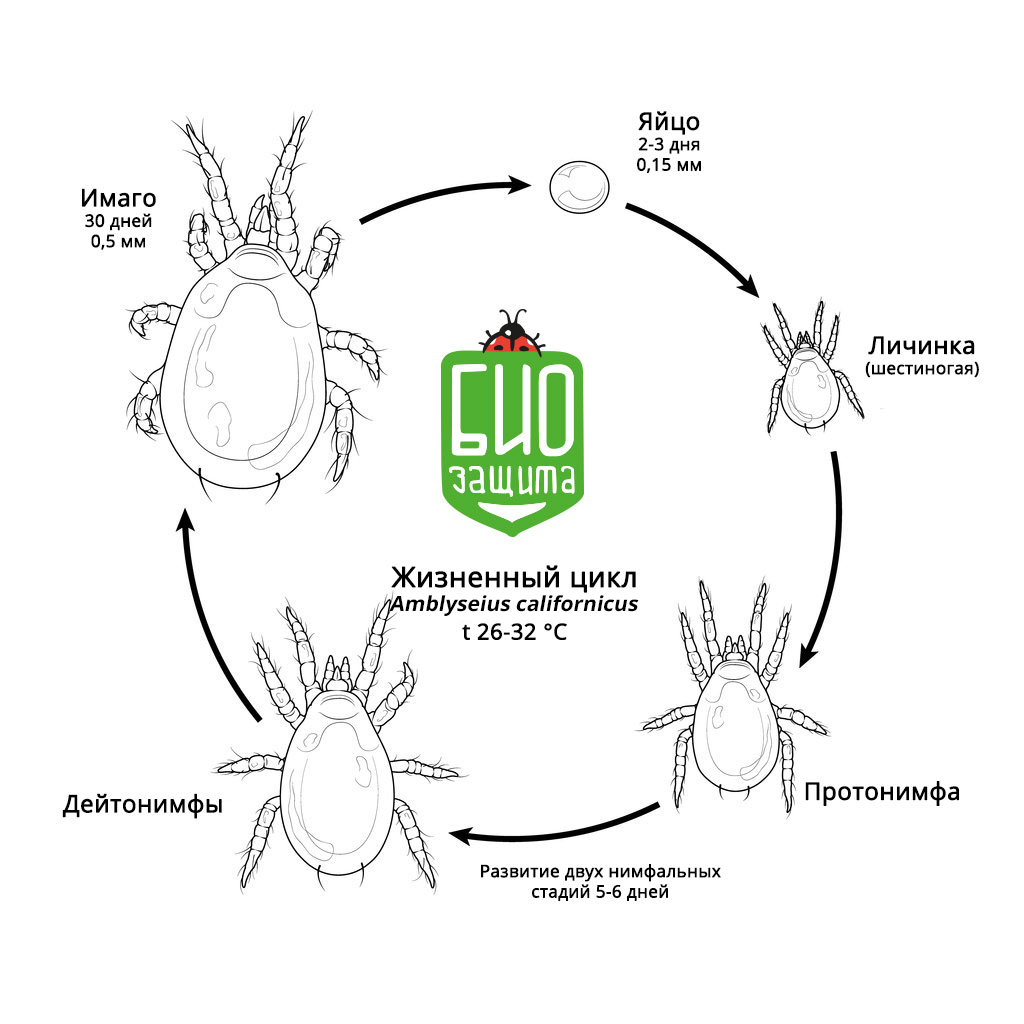
Eggs are pale whitish, spherical in shape, almost the same width along all the length. The surface of the egg is smooth and shiny, the length is about 0.16 mm. Females lay eggs under leaves, often along veins.
Larvae are pale from white to translucent color and have 3 pairs of legs. The opisthosoma has a pair of long setae. Larvae molt into protonymph without feeding.
Protonymphs are very mobile and active predators of milky-whitish color, they have 4 pairs of legs on the 2d instar of preimaginal development, body length is 0.3 mm. Before molting during the transition to the next developmental instar, the protonymph needs a little feeding.
Deutonymphs are whitish and have 4 pairs of legs on the 3d instar of preimaginal development, but they are larger and more voracious. Body length is 0.4 mm.
| Instar of development | Time of preimaginal development (days) at a constant temperature °С | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | |
| Egg | 6,07 | 2,24 | 1,61 | 1,23 | 1,14 |
| Larva | 2,71 | 0,97 | 0,78 | 0,53 | 0,5 |
| Protonymph | 5,68 | 1,71 | 1,44 | 1,1 | 1,11 |
| Deutonymph | 7,25 | 1,81 | 1,24 | 1,03 | 1,03 |
| Total | 21,71 | 6,73 | 5,07 | 3,89 | 3,78 |
Adult predators attack all instars of spider mite. Predator nymphs prefer to feed on eggs, they can hunt at other pest developmental instars. The range of A. californicus’ victims includes a variety of herbivorous mites: Tetranychus urticae, Tetranychus cinnabarinus, Tetranychus atlanticus, Tetranychus turkestani, Oligonychus pratensis, Oligonychus perseae, Oligonychus ilicis, Panonychus citri, Panonychus ulmi (Tetranychidae), Aculus schlechtendali (Four-legged mites Eriophyidae), Phytonemus pallidus, Polyphagotarsonemus latus (Tarsonemidae mites). In the case of spider mite absence, predators can attack the larvae of thrips – Thrips tabaci, Frankliniella occidentalis (family Thysanoptera).








Оставить комментарий