Glasshouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum);
Silverleaf whitefly (Bemisia argentifolii);
Tobacco whitefly (Bemisia tabaci).
Anthurium, tomato, sweet and hot peppers, rose, melon and watermelon, green and red beans, gerbera, eggplant, cucumber.
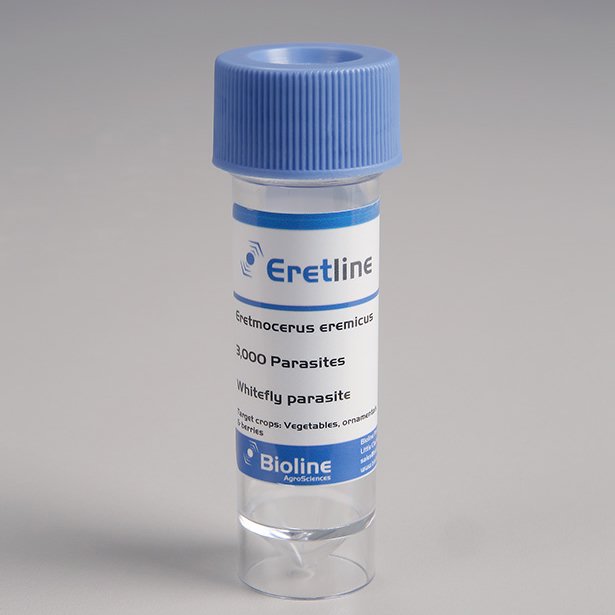
30 ml-vial contains 3 000 insects;
20 blisters contain 5 000 insects;
60 blisters contain 3 000 insects;
200 blisters contain 10 000 insects;
250 blisters contain 15 000 insects;
20 blisters contain 10 000 insects.
It is a material of European quality from Bioline agrosciences.
A wide range of packaging for easy application, depending on the specific situation.
Eretmocerus eremicus is a tiny parasitic wasp (~1 mm in length). Female E. eremicus is pale lemon yellow, male is yellowish-brown in color. Unlike E. formosa, E. eremicus lays its eggs not in the body of larva, but between whitefly larva and leaf. Females also can pierce larvae by their ovipositors and feed on the hemolymph (blood) that exudes from the wound.
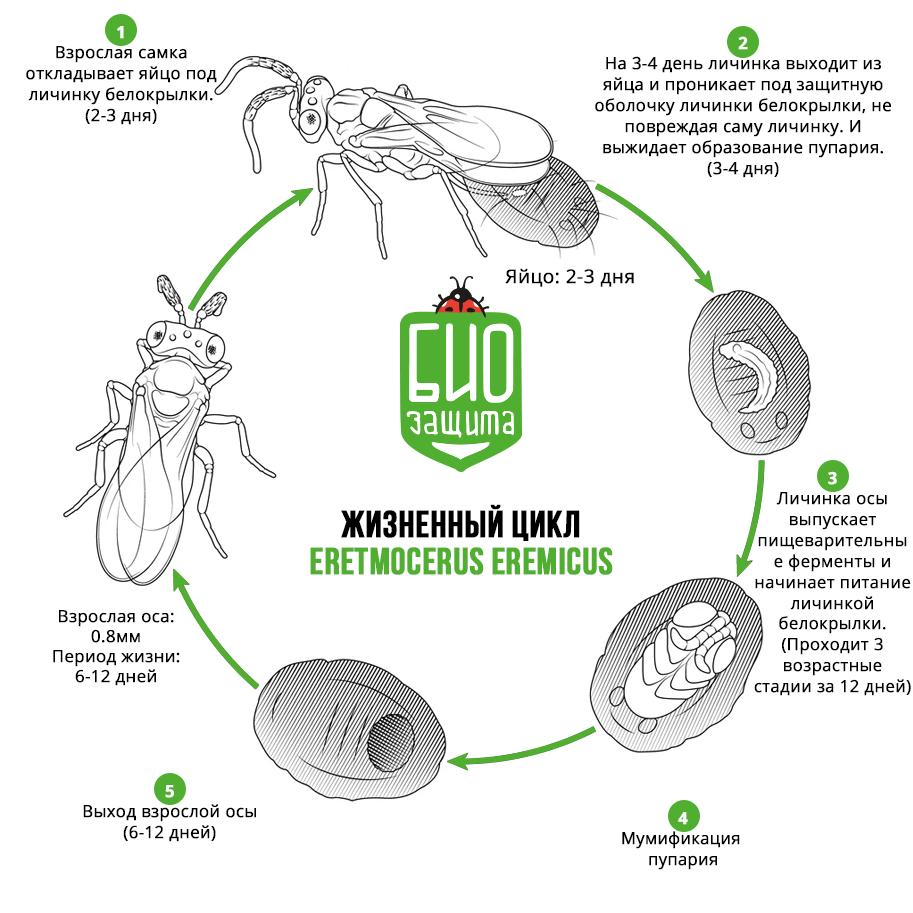
All the instars develop inside the whitefly larva. Females lay their eggs between the whitefly nymph and the leaf surface. The newly emerged larva chews a small hole into the whitefly. After 3-4 days of chewing the parasitoid larva enters the host where it remains dormant until the whitefly pupates. Once the whitefly pupal stage is reached, the wasp larva releases digestive enzymes and begins ingesting the semi-liquid body parts of the pupa.
The female lays teardrop-shaped eggs under whitefly larvae. In 3 days transparent eggs become light brown. Depending on temperature females can lay from 120 to 270 eggs.
The wasp larva passes through 3 instars. At the end of development, it fills the puparium, which turns into yellowish color, through the covers the wasp shapes are seen.
| Instar of development | Time of pre-imaginal development (days) at a constant temperature ° С | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| From egg to egg | 35 | 26 | 16 |
The adult female consumes hemolymph (blood) that exudes from the wound. In such way, the beneficial insect can kill up to 40 % of the total pest number.
Eretmocerus eremicus is produced as scattering material, as cards and blisters.
| Bioagent name in Latin | Prevention | Doses of the application by infection degree | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Average | High | ||
| Eretmocerus eremicus | – | 1 ind/m2 | 10 ind/m2 | 20 ind/m2 |
| Frequency of application | once in a month | In a week | Weekly | Weekly |



![]()
Оставить комментарий